Introduction.
Did you know that if the internet were a country, it would rank seventh in the world for greenhouse gas emissions, emitting 1.6 billion tons annually?
As a planet, we face unprecedented levels of climate change. The internet contributes significantly to this problem, consuming large amounts of electricity in data centres, telecom networks, and end-user devices. From websites to cryptocurrencies, its impact is undeniable.
Discover how web technology can remain efficient while utilizing low-carbon digital products and services.
Getting to know your digital presence.
Organizations are producing more content than ever before, such as launching websites and hosting workshops to reach a wider audience. This increases their digital footprint. While many organizations assess the environmental impact of their physical operations, such as their office space, supply chain, and business practices, they often overlook the carbon footprint of their online presence. This is a growing issue that needs to be addressed, given the rapid expansion of the internet.
Digital Beacon is an excellent tool for assessing the environmental impact of your website. It provides a score rating and breakdown of the elements that are most detrimental to the atmosphere, along with the amount of additional CO2 they contribute. We strongly suggest everyone use it as a starting point.


Our findings.
Sustainable web design is the practice of creating digital products that prioritize people and the environment. Tom Greenwood, the author of Sustainable Web Design, explains that it is a process of designing with sustainability in mind. It involves considering the environmental impact of the product, as well as the impact on people’s lives. By taking into account the long-term effects of the product, sustainable web design can help create a better future for everyone.
“Sustainable web design is an approach to designing web services that prioritizes the health of our home planet; at its core is a focus on reducing carbon emissions and energy consumption.
Business, design, and technology can be part of the solution, but only if environmental protection is at the core of key decisions and not an afterthought.”
It follows the principles of the Sustainable Web Manifesto, which calls for an internet that is:
- Clean: Services provided and used will be powered by renewable energy.
- Efficient: Products and services will use the least amount of energy and material resources possible.
- Open: Products and services will be accessible, allow users to control their data, and enable the open exchange of information.
- Honest: Products and services will not mislead or exploit users.
- Regenerative: Products and services will support an economy that nourishes people and the planet.
- Resilient: Products and services will function in times and places where users need them most.

What’s more, Tim Frick, the author of ‘Sustainable Web Design’, says:
‘Sustainable web design is a hybrid blend of environmental conservation principles and performance-based web and usability standards.
These practices can be applied throughout the lifecycle of any website, app, or online media to maximize efficiency, enhance usability, and boost performance.
Sustainable web design can reduce the environmental impact of digital products and services. This can be achieved through green hosting, measuring and reducing carbon emissions, and reducing electricity consumption.’
Sustainable web design can be put into practice by breaking it down into several categories. According to Frick, these include:
- Web Performance Optimization: How quickly do assets download to a user’s device?
- Content Findability: How quickly can users find the content they need? And how useful is that content once it’s found?
- Usability: How quickly can all users accomplish tasks across devices and platforms at various bandwidth speeds?
- Green Web Hosting: Are the servers hosting your digital products and services powered by renewable energy?
Examples from the web.
Organic Basics is an exemplary example of a low-impact website. It reduces data transfer by up to 70% compared to their standard website.
How do they achieve this? For instance, they prevent images from loading unless the user explicitly requests them. Additionally, they store data locally on the user’s device to reduce data transfer.

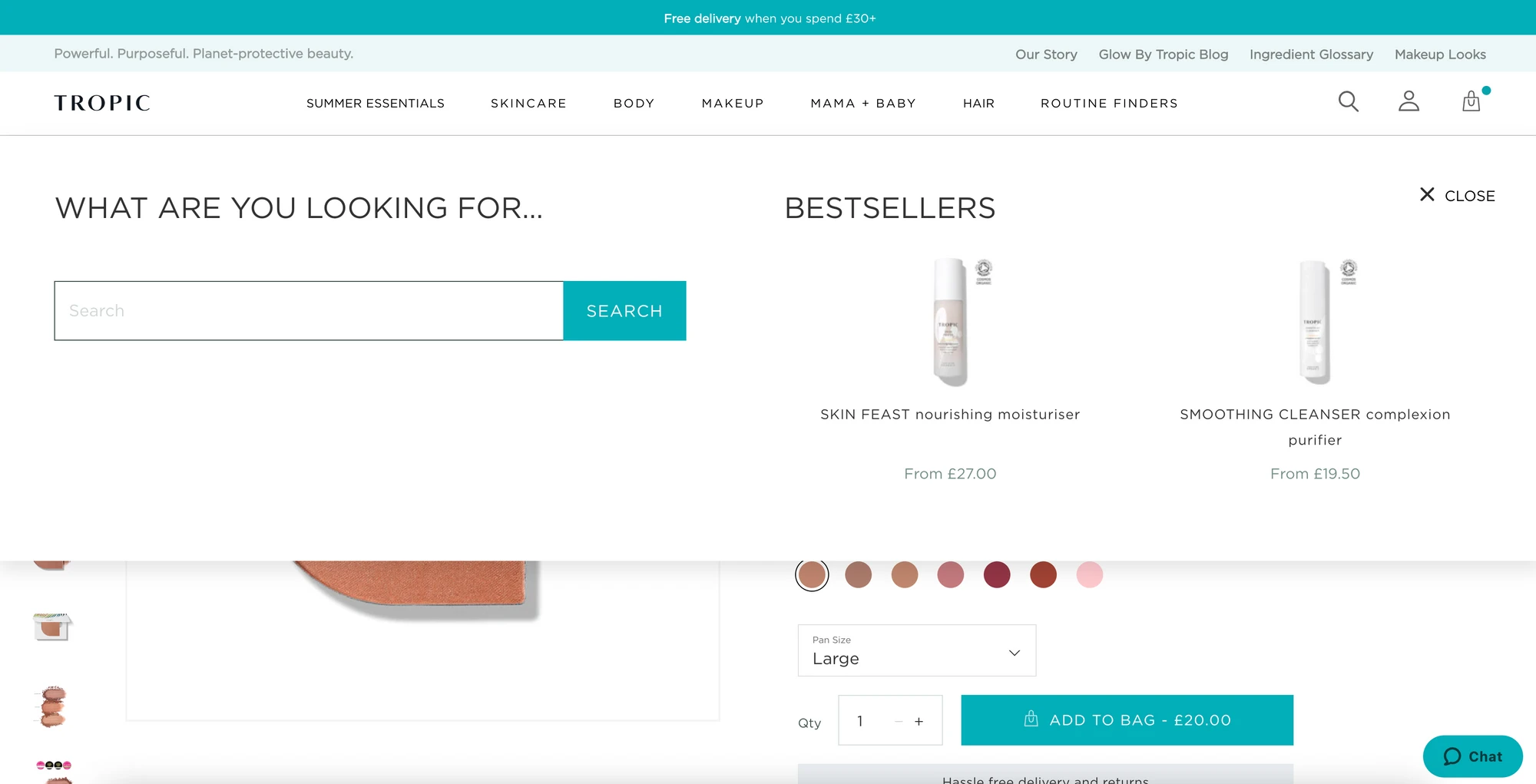
Tropic Skincare promotes sustainability through features like the ‘Product Finder’. This feature helps new users quickly find what they need, making content easily findable.
What are BURHANI doing?
Since this month Feb 2023, we’ve been looking to actively offset our carbon footprint, putting more focus on how our work affects the environment. Through Ecologi we have started to sponsor trees and begin planting small forests across the world.
We plant 100 trees for each BURHANI team birthday, up to 200 trees for each website launch, and offset our carbon emissions whenever we have team meet-ups. Em is our dedicated Sustainability Skipper and she updates us on each new planting in our #sustainability Slack channel.
Final takeaways.
The internet contributes to climate change, but there are effective strategies to reduce its impact. Web performance optimization, improved user experience, and sustainable content strategy can help. A plan can help you figure out where to start. For example, web performance optimization can help users accomplish tasks quickly and efficiently. Additionally, a sustainable content strategy can help users quickly find the answers they need. With a plan in place, you can begin making improvements.
In short:
- Choose a green and sustainable host: Google Cloud Platform is dedicated to using 100% renewable energy.
- Create a lean, energy-efficient website. Reduce unnecessary elements and optimize performance for maximum efficiency.
- Don’t autoplay videos.
- Compress images with a tool like TinyPNG or WP Smush Pro. This will help reduce file size and improve loading times.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN) to serve the correct image sizes. This will help ensure that your images are delivered quickly and efficiently to your users, regardless of their location.
- Use caching to reduce server load.
- Lazy-load content that is not visible. Doing so reduces the amount of data that needs to be loaded initially, resulting in a faster loading time.
- Delete unused files, pages and websites.
- Remember: smaller file sizes lead to faster load times, which in turn improves user experience and keeps Google happy.
Interested in working with Burhani Digital? Drop us a line at hello@burhanidigital.com.
We are a Creative Digital Agency based in Maryland, US and Hyderabad, India, specialising in Creative Web Design, Web Development, Branding and Digital Marketing.
We are also WordPress Content Management System experts.


